ABOUTELECTRIC POOL HEATERS
When it comes to heating a pool, several options exist, including electric, solar, gas, and propane heaters. However, not every heater works well for all pools, as each type has specific benefits and limitations. Deciding on the right one can be challenging. If you’re wondering how an electric pool heater operates, it’s important to first recognize that there are two distinct types: electric heat pumps and electric resistance heaters.
Electric Resistance Heaters: Electric resistance heaters generate heat by passing electrical currents through a metal resistor or heating element within the unit. As water circulates through the system, it absorbs heat from the element before being returned to the pool. This process continues in cycles until the water reaches the desired temperature.
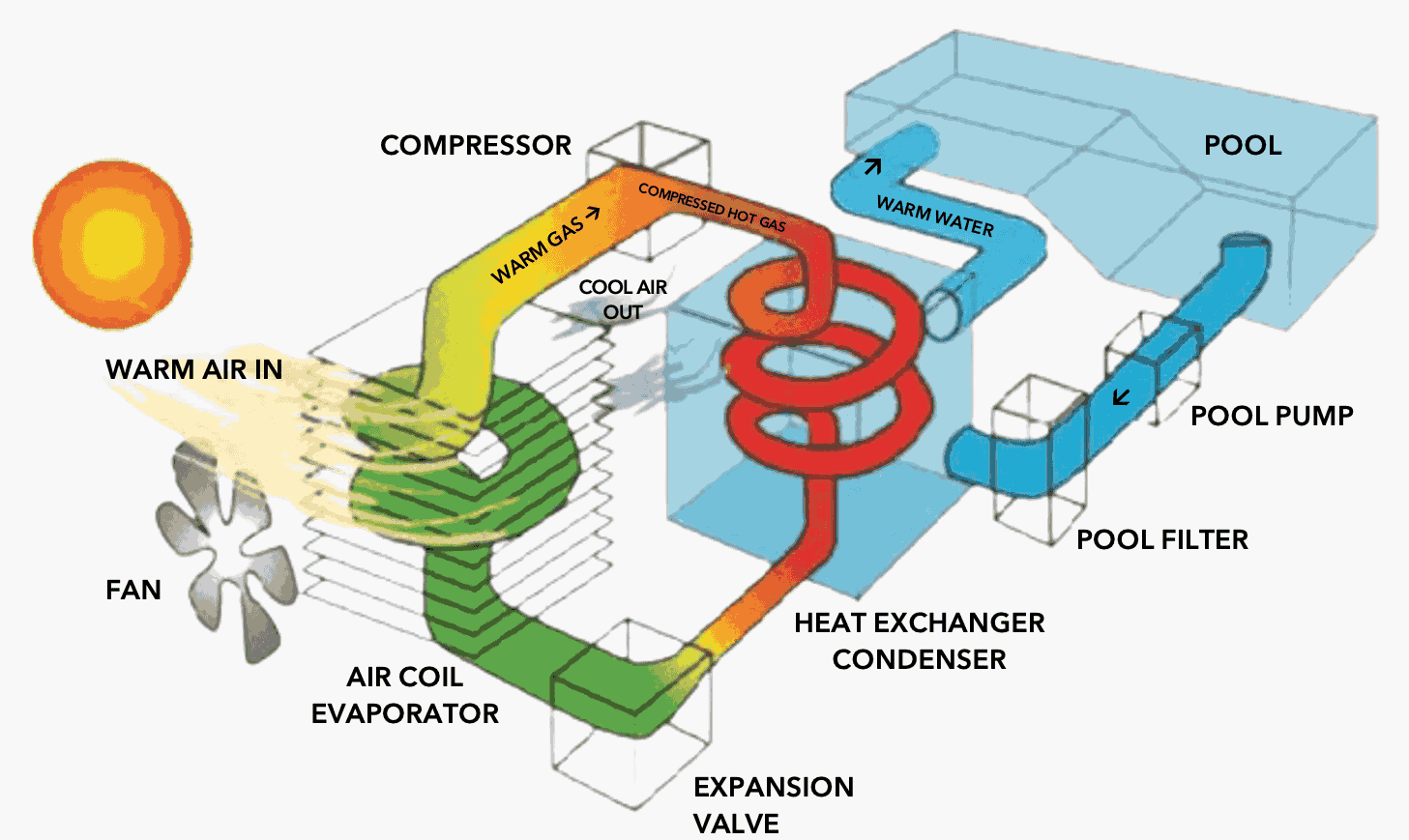
Electric Heat Pumps: The other type of electric pool heater is a heat pump, which extracts warmth from the surrounding air and transfers it to the pool water. Inside the heat pump, coils contain liquid refrigerants that interact with the captured air. As the heat comes into contact with the coils, the refrigerant converts into gas and moves through a compressor. From there, it reaches the condenser, where the water is heated before flowing back into the pool.
Apart from their reliance on electricity, electric heat pumps and electric resistance heaters have few similarities. Electric resistance heaters generate heat directly from electricity, allowing them to operate efficiently in any outdoor temperature. This makes them ideal for quick, occasional pool heating. In contrast, electric heat pumps are designed for continuous heating and are significantly more energy-efficient. During warmer weather, an electric heat pump can reduce energy costs by as much as 85% compared to an electric resistance heater. However, once the surrounding air temperature falls below 60℉, its efficiency declines.